抽象类和接口
...大约 1 分钟Java基础
- 抽象类可以包含成员变量和非抽象方法(也就是具体方法);
- 而接口只能包含常量和抽象方法,不提供实现。任何实现接口的类都必须提供这些方法的具体实现。
抽象类支持单继承,而接口支持多继承。
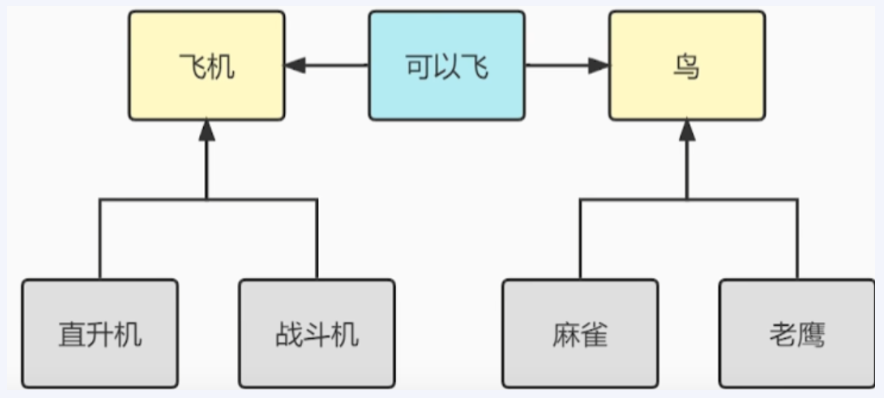
接口:自上而下,是“会”的关系,飞机和鸟都实现了“可以飞”的接口,这意味着它们都具有飞行的能力,但实现方式可能不同。 抽象类:自下而上,将某些共性的东西抽离出来,是“是”的关系。类似于图中的“直升机”和“战斗机”只能继承自“飞机”,“麻雀”和“老鹰”只能继承自“鸟”。
接口的设计目的,是对类的行为进行约束。 而抽象类的设计目的,是代码复用。
public interface CanFly {
void fly();
}
public class Bird implements CanFly {
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Bird is flying");
}
}
public class Airplane implements CanFly {
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Airplane is flying");
}
}
public abstract class Animal {
public abstract void makeSound();
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal is eating");
}
}
public class Lion extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Lion says: Roar");
}
}
public class Tiger extends Animal {
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Tiger says: Growl");
}
}
最后,可以创建一个使用这些类的示例:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用接口
CanFly bird = new Bird();
bird.fly();
CanFly airplane = new Airplane();
airplane.fly();
// 使用抽象类
Animal lion = new Lion();
lion.makeSound();
lion.eat();
Animal tiger = new Tiger();
tiger.makeSound();
tiger.eat();
}
}