Lambda表达式
01、初识 Lambda
Lambda 表达式描述了一个代码块(或者叫匿名方法),可以将其作为参数传递给构造方法或者普通方法以便后续执行。考虑下面这段代码:
() -> System.out.println("沉默王二")
来从左到右解释一下,() 为 Lambda 表达式的参数列表(本例中没有参数),-> 标识这串代码为 Lambda 表达式(也就是说,看到 -> 就知道这是 Lambda),System.out.println("沉默王二") 为要执行的代码,即将“沉默王二”打印到标准输出流。
有点 Java 基础的同学应该不会对 Runnable 接口感到陌生,这是多线程的一个基础接口,它的定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable
{
public abstract void run();
}
Runnable 接口非常简单,仅有一个抽象方法 run();细心的同学会发现一个陌生的注解 @FunctionalInterface,这个注解是什么意思呢?
我看了它的源码,里面有这样一段注释:
Note that instances of functional interfaces can be created with lambda expressions, method references, or constructor references.
大致的意思就是说,通过 @FunctionalInterface 标记的接口可以通过 Lambda 表达式创建实例。具体怎么表现呢?
原来我们创建一个线程并启动它是这样的:
public class LamadaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("沉默王二");
}
}).start();
}
}
通过 Lambda 表达式呢?只需要下面这样:
public class LamadaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("沉默王二")).start();
}
}
是不是很妙!比起匿名内部类,Lambda 表达式不仅易于理解,更大大简化了必须编写的代码数量。

02、Lambda 语法
每个 Lambda 表达式都遵循以下法则:
( parameter-list ) -> { expression-or-statements }
() 中的 parameter-list 是以逗号分隔的参数。你可以指定参数的类型,也可以不指定(编译器会根据上下文进行推断)。Java 11 后,还可以使用 var 关键字作为参数类型,有点 JavaScript 的味道。
-> 相当于 Lambda 的标识符,就好像见到圣旨就见到了皇上。
{} 中的 expression-or-statements 为 Lambda 的主体,可以是一行语句,也可以多行。
可以通过 Lambda 表达式干很多事情,比如说
1)为变量赋值,示例如下:
Runnable r = () -> { System.out.println("王二"); };
r.run();
2)作为 return 结果,示例如下:
static FileFilter getFilter(String ext)
{
return (pathname) -> pathname.toString().endsWith(ext);
}
如果不用lamada,得这么写:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取一个文件过滤器
FileFilter filter = getFilter(".txt");
// 测试过滤器
File file1 = new File("example.txt");
File file2 = new File("example.java");
System.out.println("example.txt: " + filter.accept(file1)); // 输出 true
System.out.println("example.java: " + filter.accept(file2)); // 输出 false
}
static FileFilter getFilter(String ext) {
return new FileFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return pathname.toString().endsWith(ext);
}
};
}
}
3)作为数组元素,示例如下:
final PathMatcher matchers[] =
{
(path) -> path.toString().endsWith("txt"),
(path) -> path.toString().endsWith("java")
};
如果不用lamada,得这么写:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.PathMatcher;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 PathMatcher 数组
PathMatcher[] matchers = {
new PathMatcher() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Path path) {
return path.toString().endsWith("txt");
}
},
new PathMatcher() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Path path) {
return path.toString().endsWith("java");
}
}
};
// 测试 PathMatcher 数组
Path path1 = Path.of("example.txt");
Path path2 = Path.of("example.java");
Path path3 = Path.of("example.pdf");
System.out.println("example.txt: " + matchers[0].matches(path1)); // 输出 true
System.out.println("example.java: " + matchers[1].matches(path2)); // 输出 true
System.out.println("example.pdf: " + matchers[0].matches(path3)); // 输出 false
}
}
4)作为普通方法或者构造方法的参数,示例如下:
new Thread(() -> System.out.println("王二")).start();
需要注意 Lambda 表达式的作用域范围。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int limit = 10;
Runnable r = () -> {
int limit = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < limit; i++)
System.out.println(i);
};
}
上面这段代码在编译的时候会提示错误:变量 limit 已经定义过了。
和匿名内部类一样,不要在 Lambda 表达式主体内对方法内的局部变量进行修改,否则编译也不会通过:Lambda 表达式中使用的变量必须是 final 的。
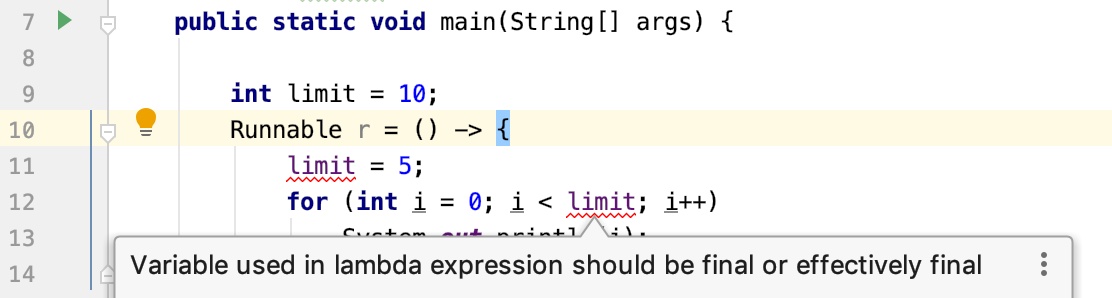
这个问题发生的原因是因为 Java 规范中是这样规定的:
Any local variable, formal parameter, or exception parameter used but not declared in a lambda expression must either be declared final or be effectively final (§4.12.4), or a compile-time error occurs where the use is attempted.
大致的意思就是说,Lambda 表达式中要用到的,但又未在 Lambda 表达式中声明的变量,必须声明为 final 或者是 effectively final,否则就会出现编译错误。