深拷贝和浅拷贝
...大约 2 分钟Java基础
引用拷贝:
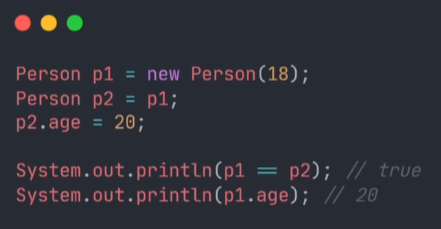
浅拷贝:
在Java中Object提供了一个clone方法,一看名字就知道他和对象拷贝有关,该方法的访问修饰符为protected,如果子类不重写该方法,并将其声明为public,那外部就调用不了对象的clone(),
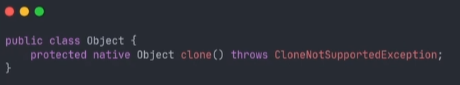
子类在重写时直接调用Object的clone()即可,它是native方法,底层已经实现饿了拷贝对象的逻辑,注意的是,子类一定要实现cloneable方法,否则就会报错。
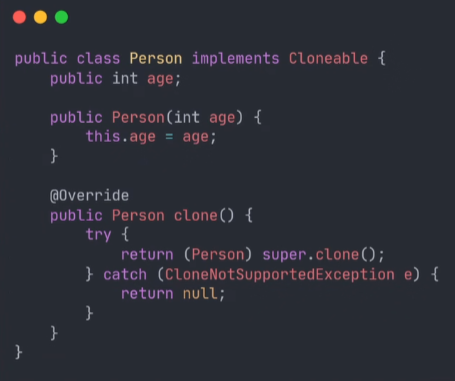
现在就可以拷贝对象了,现在已经发现两个变量指向的已经是不同的对象了。

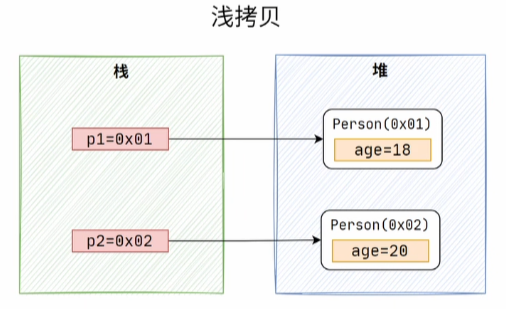
但是,有一个问题,如果拷贝的对象中有属性是引用类型,那这种浅拷贝的方式就只会复制该属性的引用地址(数组地址),如果对这个属性操作,会影响到另一个对象的属性。

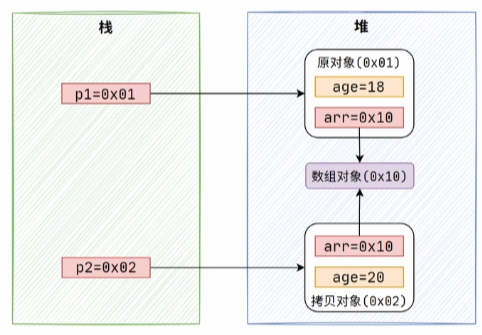
如果想将引用属性也进行拷贝,那就得用深拷贝了。
深拷贝:
实现方式有有两种方法,手动复制所有的引用对象,或者使用序列化与反序列化。
①、手动拷贝
class Person {
String name;
int age;
Address address;
public Person(String name, int age, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public Person(Person person) {
this.name = person.name;
this.age = person.age;
this.address = new Address(person.address.city);
}
}
class Address {
String city;
public Address(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Address address = new Address("河南省洛阳市");
Person person1 = new Person("沉默王二", 18, address);
Person person2 = new Person(person1);
System.out.println(person1.address == person2.address); // false
}
}
②、序列化与反序列化
import java.io.*;
class Person implements Serializable {
String name;
int age;
Address address;
public Person(String name, int age, Address address) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public Person deepClone() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 创建字节数组输出流,用于存储对象序列化后的数据
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// 创建对象输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);\
// 将当前对象(包括所有可序列化的属性)序列化写入输出流
oos.writeObject(this);
// 从字节数组输出流中获取序列化后的字节数组
// 创建字节数组输入流,用于读取这些字节数据
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
// 创建对象输入流,通过字节数组输入流读取对象数据
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
// 反序列化得到新的 Person 对象,即为深拷贝后的对象
return (Person) ois.readObject();
}
}
class Address implements Serializable {
String city;
public Address(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Address address = new Address("河南省洛阳市");
Person person1 = new Person("沉默王二", 18, address);
Person person2 = person1.deepClone();
System.out.println(person1.address == person2.address); // false
}
}
补充数据流向图:
原始对象 (this)
↓(序列化)
[ObjectOutputStream]
↓(写入字节)
[ByteArrayOutputStream]
↓(转换为字节数组)
[byte[] 数据]
↓(输入字节流)
[ByteArrayInputStream]
↓(反序列化)
[ObjectInputStream]
↓(创建新对象)
新对象 (深拷贝)